
Flush Out Excess Fluid! Diuretic Teas and Supplements Fuel a Celebrity-Backed Trend

Why the Rush for Diuretic Teas? Uncovering the Causes of Edema Affecting 30 Million People
Pursuing the Perfect Body: A Surge of Solutions in the Market
Do you notice your appearance fluctuating between slim and bloated when you look in the mirror? Do your shoes feel tight by the afternoon? Before assuming it’s a weight issue, it could be water retention, also known as edema. A simple way to check for edema is by pressing the inside of your calf for 2 to 5 seconds. If the indentation is deeper than 2 cm or doesn’t bounce back right away, it’s likely a sign of edema.
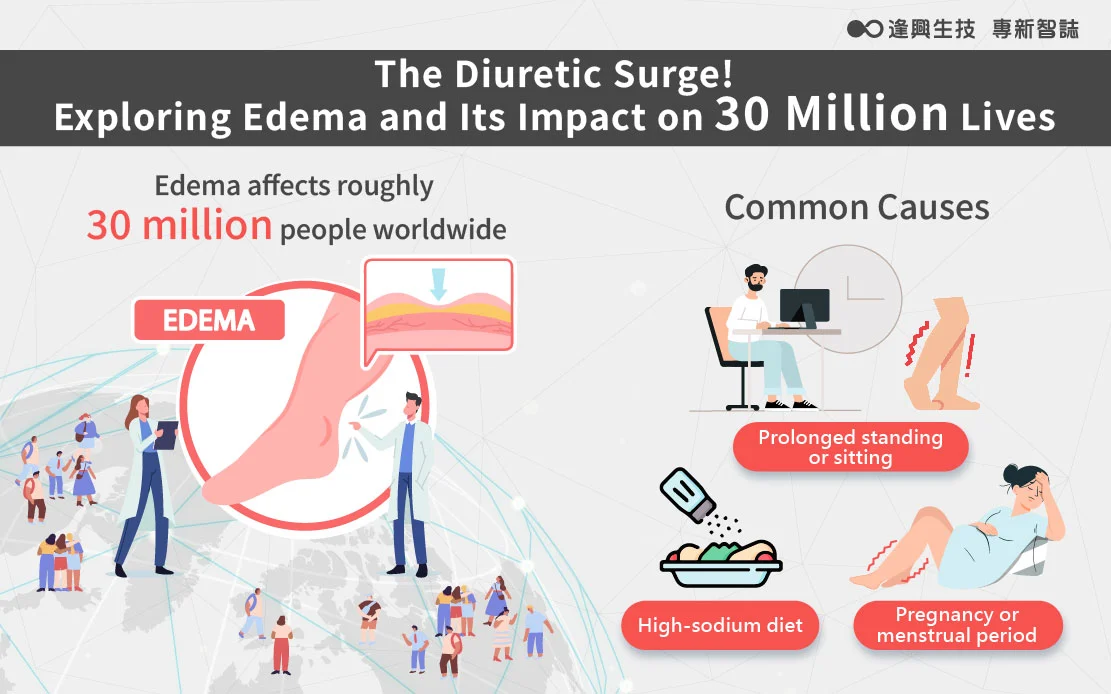
Research from the UK indicates that edema affects about 0.4% of the population[1], translating to roughly 30 million people worldwide. In a society driven by strict beauty standards, the market is saturated with remedies to combat puffiness. A popular example is Korea’s trendy ‘Fox Tea[2],’ a drink mix of red bean water and pumpkin that has taken Asia by storm. With over 20 million bottles[3] sold and US$14 million in revenue in just six months[4], the soaring demand for anti-edema products is undeniable.
Symptoms, Types, and Causes of Edema
Edema occurs when the body’s water balance is disrupted, leading to fluid buildup in the tissues—a condition similar to what traditional Chinese medicine describes as ‘dampness.’ Edema is classified into two main types: physiological and pathological. Physiological edema is often caused by factors like prolonged standing or sitting, a high-sodium diet, reduced metabolism (as seen during menstruation, lack of exercise, or irregular schedules). Pathological edema, on the other hand, may stem from issues with the heart, liver, kidneys, lymphatic system, or varicose veins[5].
Edema can also put pressure on nearby joints and nerves, causing fatigue, constipation, and poor skin health. While physiological edema can often be managed through dietary changes and increased physical activity, pathological edema requires prompt medical attention for proper treatment.
[1] Moffatt, C. J. P. L., & Pinnington, L. (2012). Project evaluation report: facilitating development of community based lymphoedema services through clinical education. East Midland Health Innovation and education Cluster, East Midlands.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6639099/#B3
[2] 在家DIY瘦身飲料超簡單!韓國減肥「狐狸茶」爆紅
https://www.elle.com/tw/beauty/health/g36593309/korea-foxwater-diet/
[3] [1,200만 완판] 여우들의 가벼운 비밀, 여우티
https://teatreat.kr/product/1200%EB%A7%8C-%EC%99%84%ED%8C%90-%EC%97%AC%EC%9A%B0%EB%93%A4%EC%9D%98-%EA%B0%80%EB%B2%BC%EC%9A%B4-%EB%B9%84%EB%B0%80-%EC%97%AC%EC%9A%B0%ED%8B%B0-%F0%9F%A6%8A/16/#prdDetail
[4] 박진호가 만난 TREND LEADING COMPANIES(2) 유귀선 바이포엠 스튜디오 대표
https://jmagazine.joins.com/forbes/view/335315
[5] Edema – Symptoms and causes
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20366493
Numerous Edema Remedies: Opt for Certified Products for Added Confidence
Remedies for Edema
- Exercise, massage, and leg elevation can help improve blood circulation and boost metabolism, reducing the effects of edema.
- Dietary Adjustments: Lower your salt intake and boost consumption of vitamins for edema, such as Vitamin B6, and minerals like calcium, potassium, and magnesium[6]. Foods good for fluid reduction include garlic, spinach, broccoli, salmon, walnuts, oats, bananas, tomatoes, and kiwis.
- Diuretic Drinks: Herbal tea for edema made with red beans, black beans, coix seeds, or corn silk, black coffee, and popular drinks like Korean idol water (cucumber and lemon), Happy Slim Water (unsweetened lemon green tea), and Fox Tea (red bean and pumpkin water).
Natural Supplements for Edema: A Convenient New Choice
Natural supplements for Edema are an excellent option. While many popular remedies for reducing edema rely on single ingredients, their effectiveness can vary based on preparation methods or the manufacturer. In contrast, natural supplements for edema offer a combination of nutrients, making them a time-saving and convenient choice for consumers who prefer certified products.
By understanding the causes of edema and incorporating exercise, diuretic foods, and natural supplements for edema, you can adopt a multi-faceted approach to reducing water retention and combating sluggishness.

[6] 6 Ways to Reduce Water Retention (Edema)
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/6-ways-to-reduce-water-retention#less-salt



